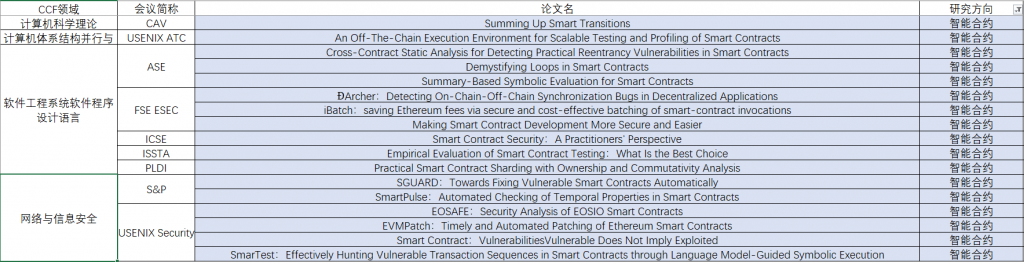
By 林岳, 2022年2月12日
论文题目:DispersedLedger: High-Throughput Byzantine Consensus on Variable Bandwidth Networks
这篇论文发表在 NSDI’2022。
- 论文作者简介
论文一作是Lei Yang,正在MIT攻读Ph.D;二作是Seo Jin Park,在MIT做博士后;三作是Mohammad Alizadeh副教授,是前两位作者的导师;四作是华盛顿大学的副教授 Sreeram Kannan;五作为斯坦福大学的教授(The Thomas Kailath and Guanghan Xu professor)David Tse。
- 论文简介
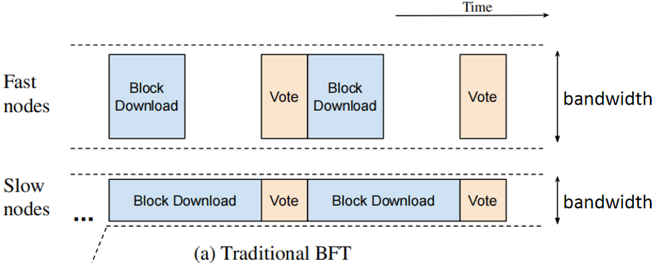
区块链中各个节点网络带宽不同,因此下载(收到)区块的速度差异较大,而传统BFT中,每个节点都要收到了区块才能够进行投票(如下图所示),即带宽大的节点收到pre-prepare(包含整个区块,消息量大)后,广播 prepare(消息量小)。但是此时带宽小的节点可能还没收到完整区块,无法广播prepare消息,而节点需要收集够 2f+1个prepare消息才能够进入到commit阶段。因此小带宽节点会拖慢共识的速度。
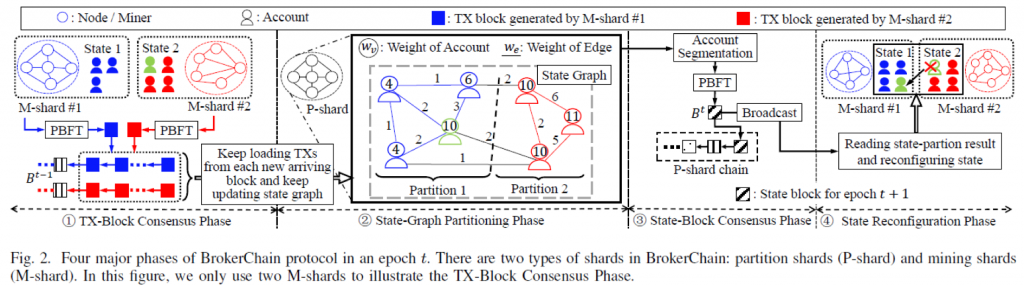
为了解决上述问题,本篇论文提出新的思路:先对区块进行共识,共识完成后节点再下载区块。这种做法的好处为:进行共识所需的带宽小,小带宽节点不会拖慢共识过程。共识完成后会进入下一个epoch,进行共识的同时节点可以下载(恢复)之前epoch的区块,这样就不会浪费大带宽节点的带宽。
一个epoch中可以有多个节点提出区块,在vote阶段通过二元共识(Binary Agreement,BA)决定将哪些区块上链。
- 关键技术剖析
(1) Verifiable Information Dispersal (VID)
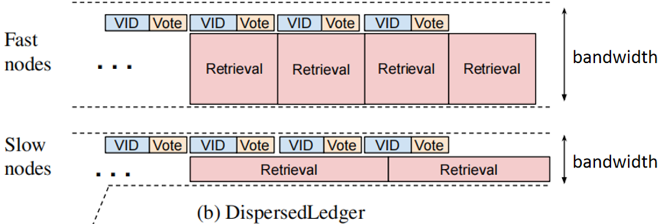
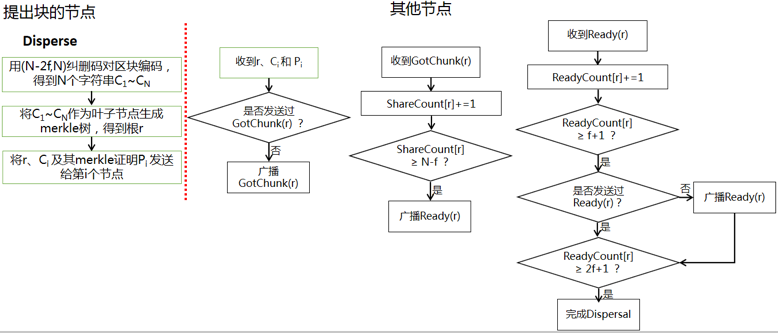
VID 就是使用纠删码(erasure code)将信息进行编码分成N份消息(chunk),每个chunk发给对应的一个节点,最终各个节点可用少于N份的chunk解码出整条信息(Retrieval)。在这篇论文中,VID阶段各个节点的操作如下图所示:
(2) Binary Agreement (BA)
由于一个epoch中,可以有多个节点提出区块,要是等到所有dispersal完成,要等待很久(甚至可能等不到,因为有拜占庭节点的存在),并且各个dispersal在不同节点完成的时间或顺序不同,因此需要通过二元共识决定最终上链哪些区块。在VID阶段完成的每一个dispersal都将会进入vote阶段,在这个阶段,节点通过二元共识最终决定这个dispersal对应的块是否上链。这里就不详述二元共识的过程,只说结果:一轮中通过二元共识最终会决定N-f个区块能够上链。
(3) Retrieval
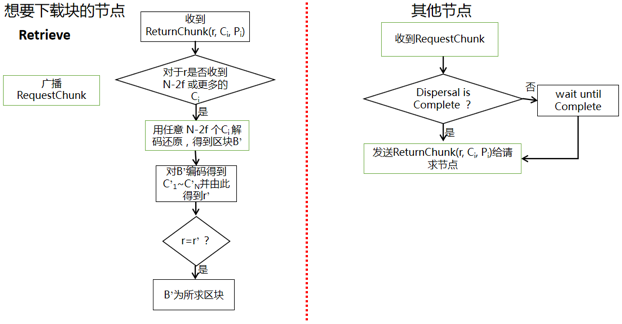
Vote 阶段结束后,各个节点就可以进入下一个epoch了,但是同时节点也要通过Retrieval去恢复之前epoch达成共识的块。也就是说共识与恢复区块是并行的,只不过共识的是以后的区块,恢复的是之前的区块。Retrieval阶段各个节点的操作如下:
(4) Inter-node Linking (IL)
注意到二元共识只会决定N-f个区块能够上链,但是未上链的区块,其dispersal可能在VID阶段已经被大部分节点完成,若在此epoch没有上链,里面的交易就要重新打包成区块在下个epoch被提出,这样做会浪费带宽。因此作者提出IL机制解决这个问题。
每个节点都会维护一个大小为N(节点数量)的数组V,V[i]标识该节点本地完成了的节点i的最大的dispersal。节点在提出块B时,会把数组V也放进区块B中。用下图举例会更容易理解。
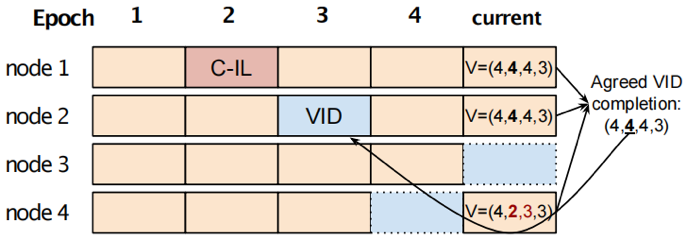
图中VID表示节点2在epoch3提出的块在VID阶段已经完成了dispersal,不过没有在vote阶段被决定上链。在当前epoch,节点4提出的块中包含了V=(4,2,3,3),说明当前节点4已经完成了节点1在epoch4的dispersal,节点2在epoch2的dispersal,节点3在epoch3的dispersal,以及自己在epoch3的dispersal,别的节点同理。在之后的Retrieval阶段,恢复出该epoch的区块后,节点4会比对各个V数组,对于V[i],取第f+1大的来更新自己的V数组(四个节点时,f=1,所以取第二大的),这样节点4就知道大部分节点都完成了图中VID所对应的dispersal,因此会去恢复图中VID所对应的区块,V数组也变成(4,4,4,3)。取第f+1大的V[i]是为了防止f个拜占庭节点作恶。
- 创新点总结
- 作者提议将共识过程与块的下载过程分开,使得各个节点都能充分利用自己的带宽,从而加快共识过程。
- 通过 IL 机制来保证正确的块都能上链,而无需重新打包出块。
- 论文的 major contribution
- 提出的VID协议比别的VID协议通信开销更小。
- 基于HoneyBadger提出的DispersedLedger,将共识与块的下载分开,使得各个节点都能充分利用自己的带宽,同时一个epoch中能够上链的块也比HoneyBadger多。
- 实验结果表明DispersedLedger吞吐量比HoneyBadger提高了105%,延迟降低了74%。
- 自己(林岳同学)的启发
- 作者是从带宽角度发现传统BFT的不足,这是我之前比较少见到的。无论多熟悉的东西,从不同点角度去看,总会有新的一些发现。
- 作者将原本被捆绑在一起的过程(下载-共识)巧妙分开并使之能够并行,这也是值得学习的。有些东西看多了就会认为其中的过程和顺序是定死的,还是得多思考,勇于思考,不要被限制住。