大家好,我想对于关注区块链动态的朋友来说,应该已经看到了昨天朋友圈被广泛转发的关于2022年福布斯全球区块链50强榜单的文章。国内的区块链自媒体也进行了翻译与转载。
我看到的两个版本分别是:来自公众号“福布斯”的《福布斯发布2022年全球区块链50强,蚂蚁、腾讯、百度等中国企业上榜》https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/YteaKOJp2qP58HwTfIO71A
稍后,公众号“区块链大本营”也进行了转载,题目为《福布斯:2022 区块链 50 强榜单》https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QSjj37_7WzBDwDkzyC85qA
本次我们以第二篇文章为基础,来聊一聊这个榜单。
文章开篇第一句话被加粗提示读者:“区块链已经走了很长一段路了!”。作为一个区块链研究者与高校的区块链课程的教师,我看到这句话的时候,愣了一下:有那么久了吗?回想一下中本聪自2008年就发表了比特币的论文,到现在区块链技术正式问世已经快14年了!的确很久了。
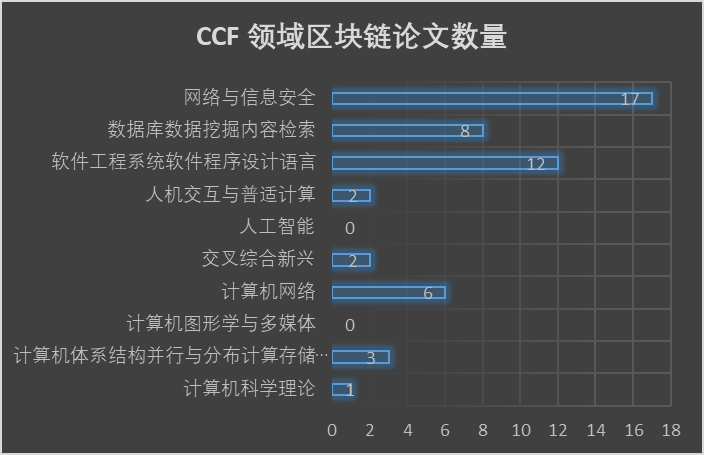
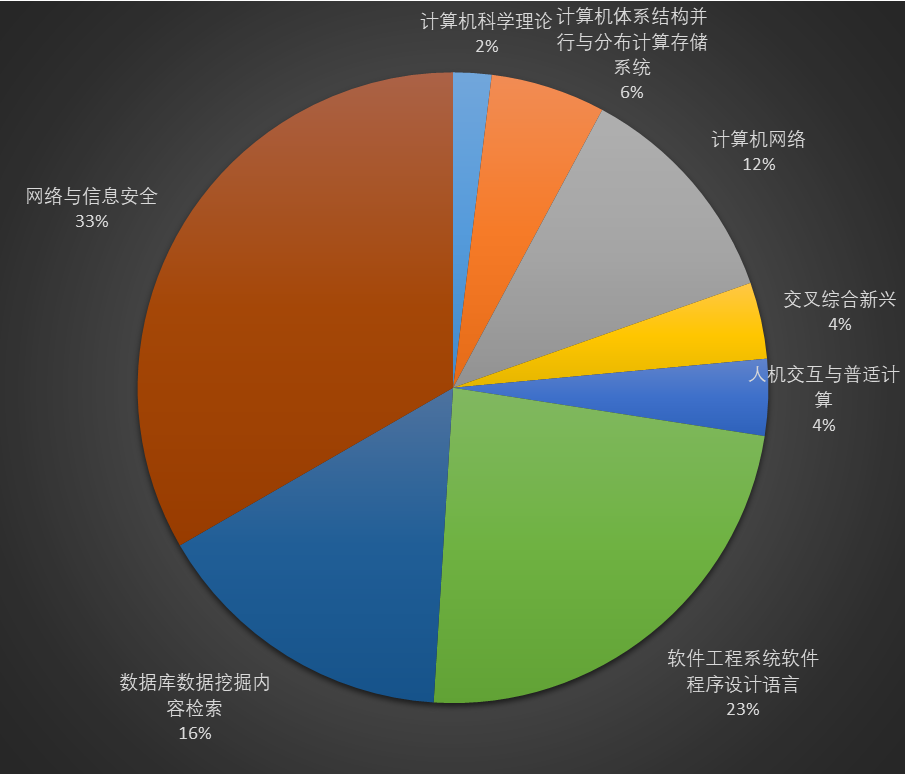
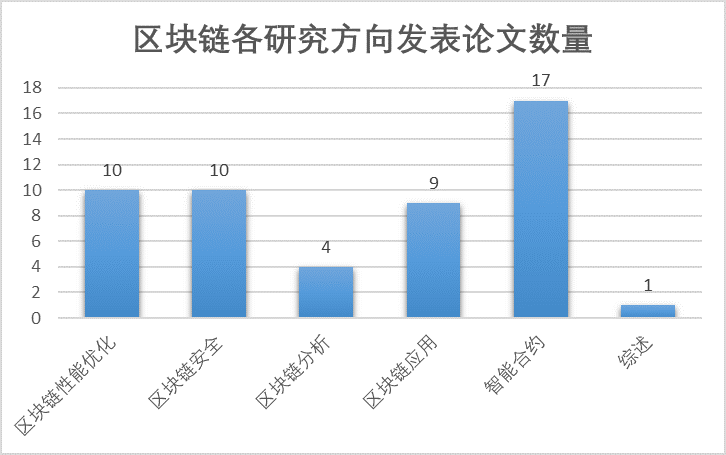
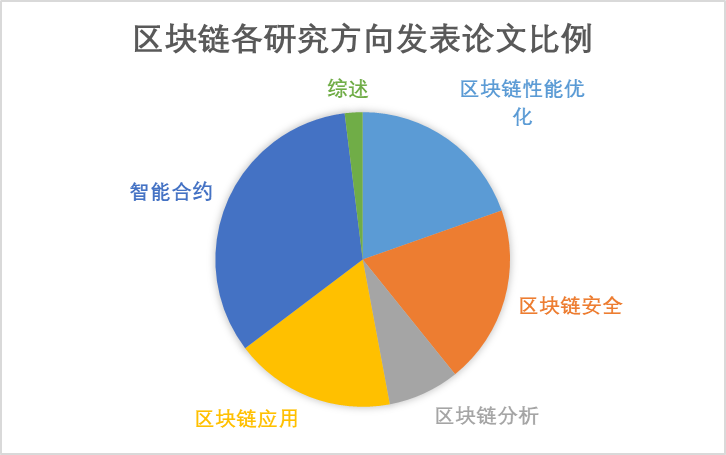
我个人是从2017年开始关注并学习区块链背后的技术原理,并逐步走上了区块链底层关键技术的研究道路。不知不觉间也已经有5年了!对我个人来讲,这也的确是非常长的一段时间了,只是平日的繁忙却掩盖了这一点,当我现在复盘的时候,也是后知后觉。还好,这5年来,我在区块链方向的研究也算是小有收获,区块链相关的研究论文有一半以上发表在计算机科学领域的顶级会议与IEEE Transactions 期刊上。这里我就不继续凡尔赛了,有机会再跟大家盘点我在区块链方向的研究成果。
我们把话题再收回来,继续看这篇题目为《福布斯:2022 区块链 50 强榜单》文章。我们了解到,福布斯从2019年就首次发布区块链50强的榜单。能上该榜单的都是十亿美元以上销售额或者市值的公司,并且强调这些公司的业务在依靠“分布式账本技术(也就是区块链技术)”来开展实际的工作。本次区块链50强榜单中几乎一半的公司的总部都设在美国以外,其中有14%是中国公司。文章还指出,今年的榜单出现的新趋势是:风险投资公司的角色越来越重,比如,风投公司在2021年向区块链行业投资了320亿美元。
该文章随即还指出,以前比特币与以太坊等加密货币常年霸占着几乎所有的区块链投资新闻的头条,尤其是当加密货币市场走牛的时候。但是自从21年11月以来,加密货币市场遭遇熊市,市值损失了超过1万亿美元。其实,投机性的加密货币是区块链技术最没有技术含量的应用。现在越来越多的公司与跨国公司逐渐将区块链整合到他们的日常运营与他们的产品中。
该文章的其他内容我们就不多转述了,感兴趣的同学可以自行前往阅读。
首先谈一下 进入到了今年福布斯区块链50强榜单的几个国内区块链头部公司,分别是 蚂蚁集团、百度、腾讯、微众银行。这里我们过一下它们各自使用或者自己研发的区块链平台:分别是蚂蚁集团的蚂蚁链、百度的开源区块链平台 XuperChain、腾讯的区块链平台包括三个即 ChainMaker、Hyperledger Fabric、以及我们很熟悉的 FISCO BCOS。微众银行的区块链平台是他们自己研发的 FISCO BCOS。
昨天 我也看到来自蚂蚁链与微众银行的合作者,在朋友圈纷纷转发了他们公司上榜的消息,在此,区块链讲师也衷心地祝贺这些业界的合作者取得了喜人的成绩,也祝愿来自企业的这些合作者们为我们中国的区块链事业做出更多的贡献!
相比之下,国外上榜的企业,大多数还是与加密货币交易相关的公司、交易所、甚至是个人建立的小型企业。比较知名的国外区块链企业包括 Coinbase、 摩根大通、Visa、Paypal、Mastercard 这些信用卡公司。
另外,榜单中竟然还有 NBA(即美国国家篮球协会)。你可能好奇,NBA为啥跟区块链扯上关系?其实,NBA 将 很多篮球相关的文化制作成 NFT 代币,然后面向广大NBA球迷进行出售、球迷们就可以 进行收藏或者交易。比如位于不列颠哥伦比亚省的 Dapper Labs 在温哥华推出了名为 Flow 的区块链,用户可以购买、出售和收集 NBA Top Shot,这些记录着 NBA 比赛精彩瞬间的 NFT 收藏品,类似于数字交易卡——比如最近以创纪录的 230,023 美元售出的 LeBron James 扣篮的 NFT。自 2020 年 11 月以来,有 130 万人创建了 Top Shot 账户,总销售额从 250 万美元飙升至 9.92 亿美元。Top Shot 的巨大成功在联盟内部引发了对加密货币的广泛好奇。NBA 专门成立了一个区块链小组委员会来评估未来的机会,推出了 WNBA (美国女子篮球联盟) 版本的 Top Shot,并与加密货币交易所 Coinbase 达成了多年的合作关系。
介绍完 NBA的情况,我们再继续看这个榜单上的国外区块链企业。当然,论美国的区块链巨头,一定少不了小扎的 Meta 公司,不过迄今为止,人们对 Facebook 元宇宙的 技术知之甚少。另外上榜的知名国外公司还有 波音公司、 Valmart、Twitter、苏富比拍卖公司。
最后,在这个榜单上我也注意到了来自亚洲的队伍在不断壮大。上榜的亚洲知名公司 包括 韩国的领军企业如三星集团和Kakao,以及日本的 富士通 和 LINE 公司。
好,今天的分享就暂且这么多。欢迎留言告诉我你的想法。
今日的话题音频记录请前往我的喜马拉雅频道收听:https://www.ximalaya.com/keji/56140880/501311859
如果你认为我的 blog 与 音频节目还不错,请动动手指,帮我分享给更多的人,谢谢大家的支持!
黄华威,2022年2月12日